Calcium carbonate, or CaCO3, comprises more than 4% of the earth’s crust and
is found throughout the world. Its most common natural forms are chalk,
limestone, and marble, produced by the sedimentation of the shells of small
fossilized snails, shellfish, and coral over millions of years. Although all
three forms are identical in chemical terms, they differ in many other respects,
including purity, whiteness, thickness and homogeneity. Calcium carbonate is
one of the most useful and versatile materials known to man.
Calcium carbonate, as it is used for industrial purposes, is extracted by
mining or quarrying. Pure calcium carbonate can be produced from marble, or it
can be prepared by passing carbon dioxide into a solution of calcium hydroxide.
In the later case calcium carbonate is derived from the mixture, forming a grade
of product called "precipitated calcium carbonate,” or PCC. PCC has a very fine
and controlled particle size, on the order of 2 microns in diameter,
particularly useful in production of paper. The other primary type of
industrial product is "ground calcium carbonate,” or GCC. GCC, as the name
implies, involves crushing and processing limestone to create a powdery-like
form graded by size and other properties for many different industrial and
pharmaceutical applications.

The main use of calcium carbonate is in the construction industry, either as
a building material or limestone aggregate for roadbuilding or as an ingredient
of cement or as the starting material for the preparation of builder's lime by
burning in a kiln. However, due to weathering mainly caused by acid rain,
calcium carbonate (in limestone form) is no longer used for building purposes on
its own, and only as a raw/primary substance for building
materials.
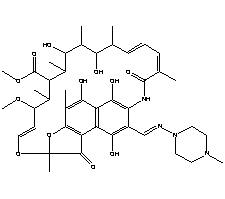
Calcium carbonate(CAS.NO:
471-34-1)
is also used in the purification of iron from iron ore in a blast furnace. The
carbonate is calcined in situ to give calcium oxide, which forms a slag with
various impurities present, and separates from the purified iron.
In the oil industry, calcium carbonate is added to drilling fluids as a
formation-bridging and filtercake-sealing agent; it is also a weighting material
which increases the density of drilling fluids to control the downhole pressure.
Calcium carbonate is added to swimming pools, as a pH corrector for maintaining
alkalinity and offsetting the acidic properties of the disinfectant
agent.
It is also used as a raw material in the refining of sugar from sugar beet;
It is calcined in a kiln with anthracite to produce calcium oxide + carbon
dioxide. This burnt lime is then slaked in sweet water to produce a calcium
hydroxide suspension for the precipitation of impurities in raw juice during
carbonatation.
Calcium carbonate has traditionally been a major component of blackboard
chalk. However, modern manufactured chalk is mostly gypsum, hydrated calcium
sulfate CaSO4·2H2O. Calcium carbonate is a main source for growing Seacrete, or
Biorock. Precipitated calcium carbonate (PCC), pre-dispersed in slurry form, is
a common filler material for latex gloves with the aim of achieving maximum
saving in material and production costs.
Fine ground calcium carbonate (GCC) is an essential ingredient in the
microporous film used in babies' diapers and some building films as the pores
are nucleated around the calcium carbonate particles during the manufacture of
the film by biaxial stretching. GCC or PCC is used as a filler in paper because
they are cheaper than wood fiber. In terms of market volume, GCC are the most
important types of fillers currently used. Printing and writing paper can
contain 10–20% calcium carbonate. In North America, calcium carbonate has begun
to replace kaolin in the production of glossy paper. Europe has been practicing
this as alkaline papermaking or acid-free papermaking for some decades. PCC has
a very fine and controlled particle size, on the order of 2 micrometres in
diameter, useful in coatings for paper.

Calcium carbonate is widely used as an extender in paints, in particular
matte emulsion paint where typically 30% by weight of the paint is either chalk
or marble. It is also a popular filler in plastics.Some typical examples include
around 15 to 20% loading of chalk in unplasticized polyvinyl chloride (uPVC)
drain pipe, 5 to 15% loading of stearate coated chalk or marble in uPVC window
profile. PVC cables can use calcium carbonate at loadings of up to 70 phr (parts
per hundred parts of resin) to improve mechanical properties (tensile strength
and elongation) and electrical properties (volume resistivity). Polypropylene
compounds are often filled with
calcium carbonate to increase rigidity, a requirement that
becomes important at high use temperatures. Here the percentage is often 20–40%.
It also routinely used as a filler in thermosetting resins (sheet and bulk
molding compounds) and has also been mixed with ABS, and other ingredients, to
form some types of compression molded "clay" poker chips. Precipitated calcium
carbonate, made by dropping calcium oxide into water, is used by itself or with
additives as a white paint, known as whitewashing.
Calcium carbonate is added to a wide range of trade and do it yourself
adhesives, sealants, and decorating fillers. Ceramic tile adhesives typically
contain 70 to 80% limestone. Decorating crack fillers contain similar levels of
marble or dolomite. It is also mixed with putty in setting stained glass
windows, and as a resist to prevent glass from sticking to kiln shelves when
firing glazes and paints at high temperature.
In ceramics/glazing applications, calcium carbonate is known as whiting, and
is a common ingredient for many glazes in its white powdered form. When a glaze
containing this material is fired in a kiln, the whiting acts as a flux material
in the glaze. Ground calcium carbonate is an abrasive (both as scouring powder
and as an ingredient of household scouring creams), in particular in its calcite
form, which has the relatively low hardness level of 3 on the Mohs scale of
mineral hardness, and will therefore not scratch glass and most other ceramics,
enamel, bronze, iron, and steel, and have a moderate effect on softer metals
like aluminium and copper. A paste made from calcium carbonate and deionized
water can be used to clean tarnish on silver.